Punjab means “five rivers”, and those five rivers are the reason that the Punjab region in Pakistan is the country’s bread basket. Tomoko and I were in Punjab last week visiting the PxD Pakistan country team. As many of you will know, PxD in Pakistan is housed within a local economics research institute, CERP, a partnership that has enabled us to be more effective and flexible.

This week much of our attention has been on smallholder rice production. The staple food in Pakistan is of course wheat (for roti), but rice is a major crop for both domestic consumption and export. (We were in town at the same time as the IMF delegation, negotiating a package of macroeconomic reforms to stabilise the economy, so those export earnings are important right now).
Punjab is famous for its basmati rice, a variety much prized for its aroma, fluffiness and grain length. It is very popular in traditional dishes like biryani and pulau. We visited Kala Shah Kaku Rice Research Institute, established in 1926, where basmati rice varieties have been developed since the 1930s. Farmers in Pakistan typically grow wheat in the Rabi season and then many grow rice in the Kharif season, especially in the basmati belt in Punjab. The yield of basmati rice is around half as much per hectare as hybrid rice varieties, but it sells for around twice the price, so generating similar revenues and broadly similar net income per hectare. (An exciting development on the horizon is the prospect of hybrid basmati rice that may have a much higher yield while retaining much of the quality for which basmati rice is famous.)
Many of the people we met were keen to stress that Pakistan, rather than India, is the home of basmati rice. I’d be very glad if the rivalry between these two great nations were confined to arguing about the origin of basmati rice and, far more importantly, their relative prowess in cricket.
Pakistan’s farmers produce on average around 4 tonnes of rice per hectare, about the same as in India. In China, the yield is 7 tonnes per hectare and in Australia 10 tonnes per hectare. The yield gap (that is, the gap between what farmers produce and what they could produce with the land and other inputs available to them) is estimated to be about 50% – about 3.5 tonnes per hectare – for basmati rice, and closer to 60% – 6 tonnes per hectare – for the higher yield but lower price varieties. In other words, farmers could, in principle, at least double their yields. So what is holding them back?

You would expect farmers to be more interested in increasing their profit than their yield, so one possible explanation – in theory – could be that the additional inputs are too costly, and the value of the extra output does not justify the investment. In that case, it would be rational for farmers not to increase their output this way. But that doesn’t seem to be the problem. The additional cost of the recommended inputs, at market prices, is small relative to the price that basmati farmers could get for the roughly extra 3-4 tonnes per hectare that they could be producing. Despite extra input costs, the extra yield on this scale would lead to much higher profits – perhaps multiples of profits now being earned. If you are doing only a little better than breaking even, then moving to a reasonable surplus could mean a transformational increase in net income.
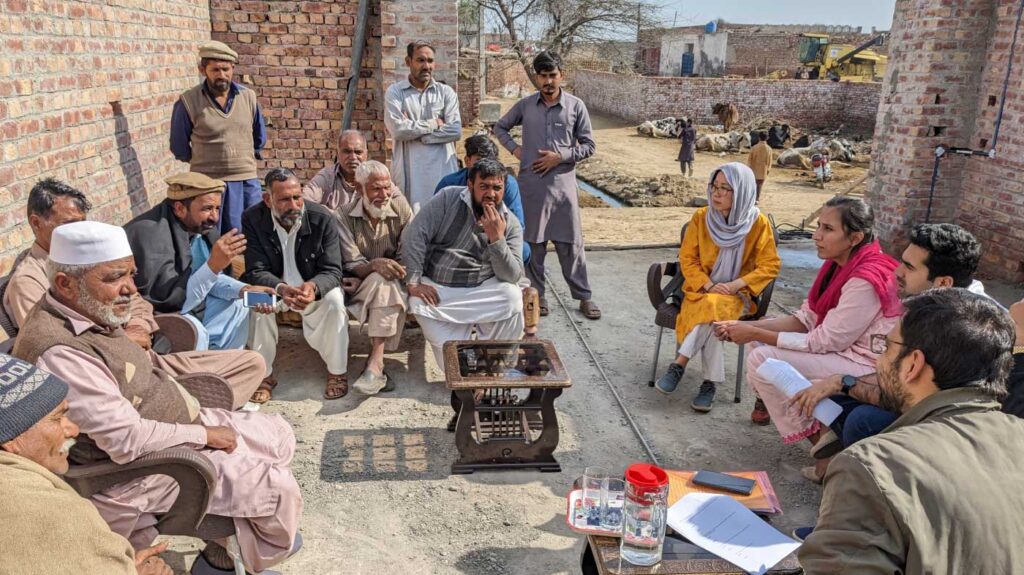
So what is getting in the way? We spent two days in villages outside Lahore talking to farmers, extension agents, and private and public sector experts to try to get a better picture.
My main take-away is that it seems that expensive credit for agricultural inputs and low prices paid by middlemen (called aahrtis) leaves farmers with little surplus. Farmers are unwilling to take on a large, expensive debt which – if the harvest is bad – they may not be able to repay, especially when they know that a big chunk of any profit, if the harvest is good, will go to the middleman. So they stick to limited use of inputs, which gives them lower yields and less debt and thus lower risk. Thus it is the cost of credit, and the associated risk, rather than the cost of the inputs themselves, that stops them from investing more.

I’m conscious that we met farmers close to Lahore, who are relatively well-off, and who are already in contact with extension services. So we should be careful about drawing too many conclusions. Based on these few conversations with an atypical group of farmers, I find it hard to convince myself that there are very many practices that farmers could adopt that they do not already know about. That said, there may be some value to encouraging practices that cost the farmer little or nothing to implement – or which save inputs such as using the right amount of urea – for example by issuing timely reminders. But it looks as if the larger gains would come if we could find a way to reduce the risk of increased investment in inputs, reduce the cost of credit, provide high-resolution weather information, or perhaps improve planning and coordination in the use of scarce machinery or casual labour.
It is harder to notice what is missing than what is in front of you. As you may see from the photos, we did not meet any women farmers. We met a female scientist at the rice institute, but everyone else we spoke to was a man. In every conversation, farmers were routinely and unthinkingly referred to as “he”. Yet we know that women provide a substantial part of labour in agriculture, and are hugely affected by all the decisions that are made. If we want to understand what it would take for farmers to adopt practices that would increase their yield and their incomes, we are likely to learn a lot by talking to women too.

I leave Pakistan optimistic but uncertain. Optimistic because the opportunities are huge for large increases in yield and potentially transformative increases in farmer incomes. The constraints are real, but there may be solutions that have a low marginal cost per farmer and so would be hugely cost-effective at scale. Uncertain because we do not yet have enough information to arrive at robust ideas for higher-impact services that we could design and test.
I want to thank Adeel, and all the team, for giving up so much of their time and energy to host us – including taking us to the old Walled City of Lahore to have dinner overlooking the famous Badshahi Mosque (Mosque of Kings) and the Lahore Fort (Shahi Qila in Urdu), an ancient citadel of the Mughal Empire. I look forward to returning to Pakistan soon and hope to combine my next trip with some tourism in your beautiful country.

When disease and a heatwave, followed by devastating floods ravaged Pakistan’s Punjab province, PxD’s LMAFRP digital information service, which we implement in partnership with the Rural Community Development Society (RCDS) with support from the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), assisted women livestock farmers navigate new and unprecedented challenges. This International Day of Rural Women, we highlight the important role women play in Punjab’s rural farming economy and our work to promote information to enhance more productive and resilient livelihoods.

Introduction
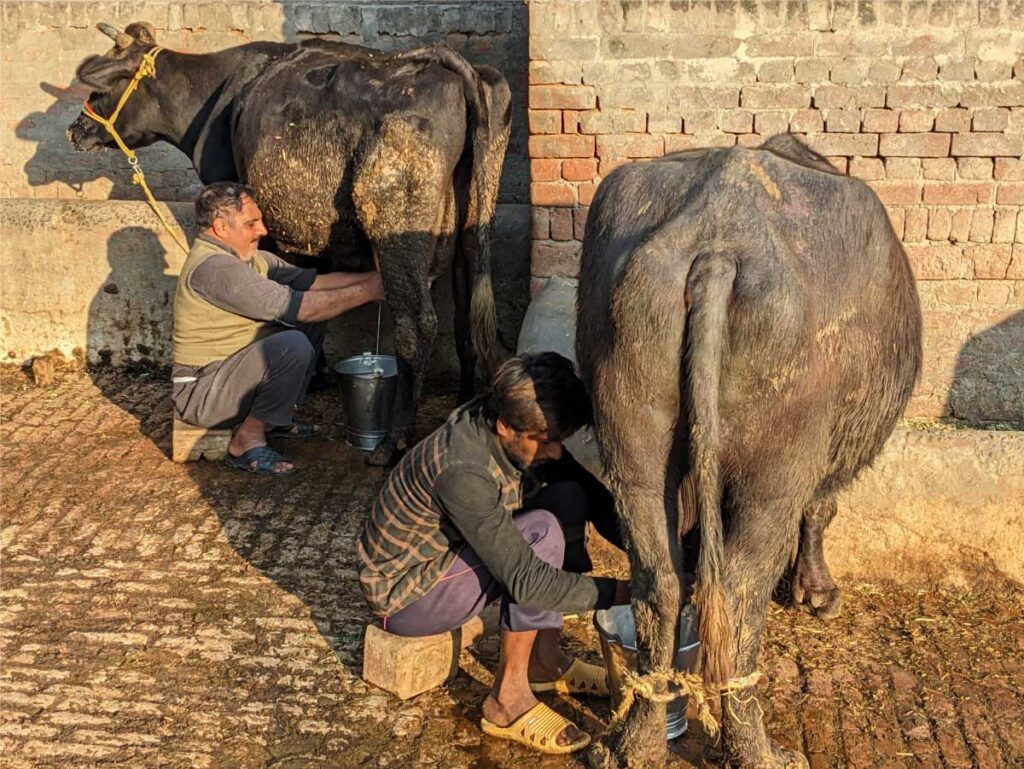
Livestock husbandry and livestock-related products (dairy, meat, leather goods, etc.) constitute an important sub-sector of Pakistan’s agriculture sector: Pakistan is the fourth largest milk-producing country in the world1Sattar, Abdul, “Milk Production in Pakistan” PIDE Blog, pide.org.pk/blog/milk-production-in-pakistan , and the share of livestock products in the generation of foreign exchange is approximately 13%2Government of the Punjab, “Livestock Contribution” , livestock.punjab.gov.pk/livestock-contribution. As is the case in many smallholder economies, in Pakistan, women are largely responsible for the care of livestock and for the production of many livestock-related products, particularly dairy3Ibid..
In rural areas, livestock plays an outsize role in livelihoods, with the Punjab provincial government estimating that “livestock is an integral part (30-40%) of the livelihood of about 30 to 35 million rural farmers”4Ibid.. Livestock-related products, such as butter, eggs, meat, and animal fats (oils), contribute important nutrients for all households – rural and urban – and play a critical role in meeting the nutritional needs of rural children. Further, livestock contribute an important source of continuous income which can sustain poor rural households between seasonal crop-related revenues, and insulate them from shocks5Ahmad, Tusawar Iftikhar and Tanwir, Farooq, “Factors Affecting Women’s Participation in Livestock Management Activities: A Case of Punjab-Pakistan”, mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/93312/1/MPRA_paper_93312.pdf..
For these reasons and more, supporting the development and improvement of livestock farming can have a considerable impact on improving the livelihoods of Pakistan’s rural population, and can impact the livelihoods and status of rural women. We believe significant gains can accrue to rural farming families through the promotion of best practices to women. Improved practices can improve yields and minimize losses, leading to increases in income from livestock farming.
Many rural women are unaware of best practices that can optimize outputs associated with livestock, and access to information and economic opportunities can be constrained by cultural and geographic barriers. As documented elsewhere on this blog, digital extension services offer cost-effective and easily scalable solutions with very low marginal costs. In rural Pakistan, where many women rarely leave their homesteads, the portability of digital information offers additional advantages for navigating geographically and culturally hard-to-reach spaces.
Geographic and cultural constraints to attending in-person RCDS livestock training sessions were exacerbated by social distancing introduced to mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic. RCDS’s in-person activities were suspended in the initial months of the pandemic, but the utility of advisory information increased as rural households navigated new challenges in a time of escalated economic stress. It was at this time that RCDS and PxD initiated a partnership to deliver advice to livestock-rearing women in rural regions of Punjab province in Pakistan. This collaboration, supported by IFAD, provides customized and actionable digital information to livestock-rearing women. Combining PxD’s experience in delivering digital extension services to Punjabi farmers and RCDS’s extensive local knowledge and expertise, the service draws on demographic insights, and cultural practices to deliver information that is accessible, comprehensible, and actionable for recipients.
The resultant digital advisory service has proven to be an effective, cost-efficient, and scalable supplement to in-person training, and is now extended in the absence of COVID-19-related social-distancing constraints. The service demonstrated new advantages when unfamiliar disease- and climate-related threats subsequently impacted rural households.
The Service
RCDS’s experience and local trust in their services have been integral to the success of the initiative. Over the past two decades, RCDS has partnered with local, federal, and international institutions to build a significant rural network to promote and implement development programs to assist poverty-stricken segments of society in rural areas of Pakistan.
Advisory content was developed in partnership with local livestock consultants who were well-informed about local livestock issues and output-increasing best practices. The advisory information distributed by the service covers a wide array of topics, including disease identification, information about and access to vaccinations, disease prevention and remedies, practices to increase milk yields, and guidance on protecting livestock against climate-related shocks.
After conducting a baseline survey to systematically understand the informational needs of women farmers in four districts in Punjab, and the development of advisory information, PxD piloted digital services among 3,160 rural women associated with RCDS. The four districts, in which the pilot was concentrated, are among the poorest districts of Punjab, all of which are located in the south of the province. Given the success of the initial pilot, the service has subsequently been expanded to more than 50,000 livestock-rearing women in 16 rural districts of Punjab.
One of the key components that PxD assessed during the initiative was the extent of knowledge retention by participating women after they received the advisory. Pilot testing in the early stages showed that the advisory information was not only useful but was also retained for a significant period after it was delivered.
RCDS maintains a dataset of women who have either attended in-person sessions of livestock advisory or shown an interest in livestock advisory or have taken a microfinance loan for livestock farming. This data, and its quality, were instrumental in helping PxD deliver the advisory directly to the women via their phones. Furthermore, the data also contained the districts in which each woman resided. This was used to help decide in which of the two local languages – Punjabi and Saraiki – the advisory would be conveyed.
Advisory information is delivered through a voice call. A text message is sent 24 hours before the call to alert users that they should expect a call the next day. This is done to ensure that the advisory is received by women. A barrier highlighted by the baseline survey was limited access to mobile phones on the part of women in the region. Cultural and financial constraints make it far more likely that men have primary access to cell phones. Hence, the time allotted for the voice calls is set at a specific hour in the evening, so that the call is received in the evening when the family is no longer busy with agricultural activities, men are more likely to be home, and when family members can collectively listen to the advisory in their homes.
The voice call has local cultural music layered in the background, to assist the participant in developing trust in and comfort with the message. The information is delivered in the local dialect – Punjabi or Saraiki – to enhance understanding of and familiarity with the recorded message. Further, listeners are told that the advisory is from RCDS since it is well-known as a trusted organization in these regions. As a general protocol, to improve pick-up rates when the voice call is unanswered, another call is placed after a 15 to 30-minute interval.
Lumpy Skin Disease
A significant advantage of digital extension is the ability to send timeous information. This is particularly valuable to address and prevent viral diseases that can have a drastically negative impact on the well-being of the livestock.
In April 2022, Pakistan saw a viral outbreak of lumpy skin disease in cattle. The disease was transmitted between cattle via blood-feeding insects. The disease has a high virulence and fatality rate and killed thousands of cattle in the country.
A significant hurdle that seriously hindered timely prevention and actions to curtail the impacts of the infestation was the lack of baseline knowledge and awareness of the disease. Moreover, misinformation was rife, with misplaced rumors about negative effects of vaccines abounding. Many people mistakenly believed that it was the vaccines that were causing deaths among animals, when animals that had died were either already infected with lumpy skin disease, or were generally sick and should not have been vaccinated at the time.
Understanding these knowledge gaps, PxD and RCDS collaborated to provide timely information about the infestation. Initial infections were observed in the southern part of the country and slowly spread north towards Punjab province, where our users reside. PxD started providing information about lumpy skin before the disease had become widespread in the province.
Our farmer-users were given information about the disease and its virulence, how it is spread, and traditional preventative measures. Following that, to increase the survival rate of infected cattle, users of the service were advised to vaccinate their cattle as soon as vaccines became available. Participants were also informed about how to identify early signs of the disease on the animal.
Anecdotal feedback received by RCDS in the field suggests that the messages were very useful. Users with whom PxD surveyed reported that in many instances they were able to avoid fatal infections in their animals due to timely vaccines, even if their animals did get infected.
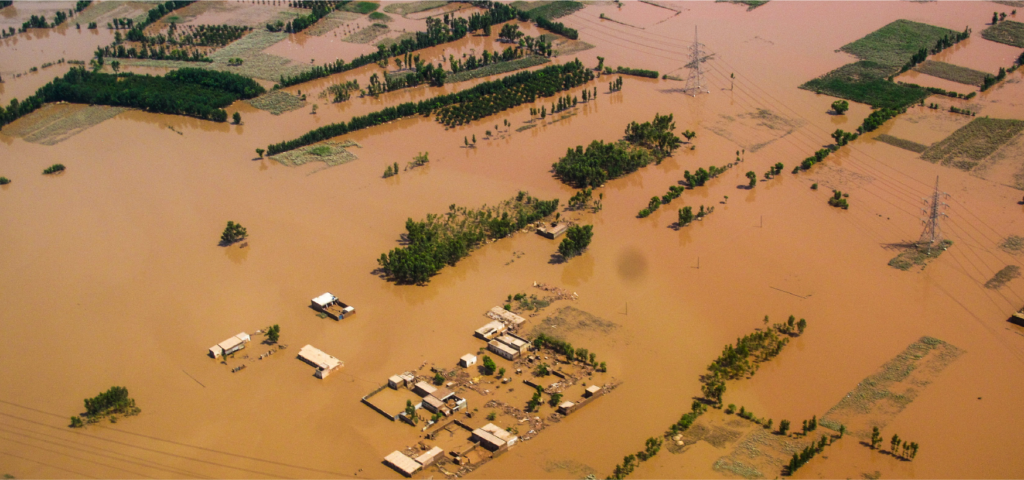

The Floods
In the summer of 2022, Pakistan witnessed firsthand the severe impacts of climate change. In March and April, the country experienced a crippling heat wave, followed by a record-breaking monsoon season in Punjab, Sindh, and Balochistan spanning June, July, and August. An unparalleled monsoon, coupled with unprecedented melting of glaciers in the north due to the initial heatwave, led to extreme flooding in rivers that flow from the north of Pakistan to the south. The floods are estimated to have impacted at least one-third of Pakistan, including the livelihoods of 33 million people.
Prior to the floods, the extreme heat waves had contributed to a general belief that floods were imminent. To counter the threat, the PxD team in Pakistan worked with RCDS to preemptively identify areas prone to flooding, and prepare advisory messages with useful information about managing floods, and adaptive strategies to protect assets and livelihoods.
A major problem with livestock is their slow mobilization, making them and their rearers prone to becoming flood victims. Timely warnings and regular updates via voice call advisory messages provided participants with information for ensuring the safety of their livestock during the floods. PxD and RCDS made use of their existing program to deliver instructions, warnings, measures, and assistance via voice call messages, to inform participating women and their families about floods and ways to protect themselves and their livestock.
Meeting today’s challenges
The advisory service designed by PxD, and delivered in partnership with RCDS, provided an effective method to deliver timely information to livestock farmers. Due to its effectiveness in the regions where it was being delivered, the advisory service was extended to address other unforeseen challenges, such as the virulent lumpy skin disease, and flooding.
In addition, our project has demonstrated the core strengths of digital communication: it is cost-effective, scalable, and capable of reaching regions and communities that are disconnected or hard to access due to difficult terrain, long distances, or cultural constraints.
Our advisory content was designed to deliver information in a manner that does not require the recipient to have prior knowledge, or education to understand the subject. The use of familiar dialects and carefully crafted messages made the information accessible, easy to understand, and ultimately very effective.
PxD aims to further extend the benefits of digital communication to support other low-cost interventions among rural communities of Pakistan. More specifically, feedback received from users has prompted PxD to further our partnership with RCDS to envisage interventions to support digital veterinary services. We are motivated to continue to harness the power of digital communication to facilitate more productive and resilient livelihoods in rural communities of Pakistan.
Precision Development (PxD) recognizes that the informational needs of poor women farmers, and the challenges they confront, are unique. As a consequence, our services must be tailored to reach and be relevant to the needs of women users. Driven largely by the onboarding of women active in livestock-related activities, the number of women farmers active on platforms built by PxD increased by approximately 46% over the course of 2021. This included the onboarding of over 150,000 women farmers to our Ama Krushi (AK) service, which we deliver in partnership with the Government of Odisha, India. As we mark International Women’s Day, we reflect on efforts we have made to improve our understanding of gendered divisions of labor and bargaining power within Odishan smallholder households, and steps we are taking to assist women farmers make more informed decisions.

Scoping work undertaken by PxD suggests that women farmers spend more productive hours on livestock farming than men. However, women farmers disproportionately lack access to mobile phones and, by extension, digitally conveyed information. Perhaps the largest impediment to increased engagement with PxD’s advisory on the part of women farmers is access to information, and patterns of information sharing within households. This could have knock-on effects that undermine women’s productivity and bargaining power within the household. To further understand these dynamics, we explored if sending messages encouraging information sharing within households can assist in breaking this cycle.
The motivation
Gendered roles in livestock farming
In June 2021, we conducted a survey to improve our understanding of gender roles in livestock farming in Odisha. The sample consisted of 5,354 AK farmers who have subscribed to livestock-related advisory, practice cow-rearing, and had received at least one livestock advisory message via the AK service. The sample included equal numbers of male and female users and was stratified by the farmer’s district. Of this sample, we successfully surveyed 1,475 AK farmer users.
We found that, on average, women AK users allocate more time to livestock rearing and household chores than male AK users (Table 1). Relative to male AK users, women spend less time on cropping activities and on other non-livestock-related income-generating activities.
The survey also found that men AK users are significantly more likely to perform—and be the primary decision-maker for—livestock-related tasks that require travel outside of the home. These types of activities include veterinary visits, purchases of livestock-related inputs, selling milk, and sourcing fodder. Women, on the other hand, are more likely to be involved in livestock-related activities performed at home, such as cleaning sheds, feeding, and milking animals. Given the heavy involvement of women farmers in livestock-related activities, it is important that livestock advisory broadcast via our AK service is communicated to women household members if it is to be practical.
Importantly, many income-related improvements in livestock outcomes—such as increasing milk yields and successful breeding—depend on the coordination of multiple tasks performed by both men and women within a household. For example, successful breeding requires the completion and timely sequencing of tasks and processes, including the provision of sufficient nutrition, deworming, heat detection, and accessing artificial insemination (AI) services. To achieve these ends, it is important that livestock advisory reaches both women and men in the household, and that intra-household communication is sufficient to coordinate improved livestock outcomes and household welfare maximization.
Barriers to information for female farmers
Reaching female farmers through mobile phone extension services is challenging as men farmers are more likely to be the primary owners of mobile phones in the household (OECD, 2018; Baroni et. al., 2018). Evidence suggests that women registered as subscribers to PxD’s mobile advisory services have shared access to phones and male partners are the devices’ primary users. PxD uses polling surveys to maintain and improve quality service delivery, and to source feedback from users. Women AK users polled for our May 2021 livestock survey self-reported lower pick-up rates than male respondents. However, actual outbound AK administrative data does not reflect a gendered disjuncture in pick-up rates. An explanation of this could be that the household member who picked up the phone when an AK call was placed to a women farmer was not the registered woman user. Similarly, during this gender survey in Odisha, we asked the respondent who picked up the phone if they were the registered AK user. In the case of registered women AK users, someone else picked up the call 12% of the time, compared to only 5% in the case of registered men AK users. This difference is statistically significant at the 1% level. This suggests that when a phone is being shared, registered users that are women have less time with the phone than men. Given the greater engagement of women in livestock-related activities, this gendered barrier in mobile phone extension services is a significant challenge.
To gather more evidence on AK users’ individual access to mobile phones, we asked about a quarter of the AK users in the Gender Scoping Survey (n=370) about their typical access to mobile phones between 6 a.m. and 9 p.m. every day. Women AK users reported less availability at all times of the day (Figure 1). However, the difference is only statistically significant at the 10% level for the 3 p.m. to 4 p.m. period (both in the full sample and the married-only sample). Due to the smaller sample size, we may be underpowered to detect other differences.
Figure 1: Gender differences in individual access to phone
Interestingly, when we restrict the analysis to household heads only, women report higher average access to their mobile phones than men. The Gender Scoping Survey finds that the time-use patterns of women heads of households closely follow those of men heads of households (Table A1), there are a few possible reasons for this deviation in self-reported access to mobile phones. A possibility is that male heads of households are more likely to share their phones with their spouses or children. By contrast, the Gender Scoping Survey found that women heads of household are typically unmarried (or widowed, separated, or divorced) and therefore may not need to share their phones as much as men heads of household.
Consistent with the evidence above, the Gender Scoping Survey finds that men AK users are significantly more likely to cite Ama Krushi as a primary source of livestock information than women AK users (Table 2), while the polling survey finds that women AK users are significantly less likely to answer knowledge questions based on livestock advisory sent in the month preceding the survey correctly.
Importantly, AK users seldom cite their spouses as a source of livestock information or as someone they discuss new livestock information with, a gap in intra-household information transfer that PxD could potentially influence. Improving intra-household communication can potentially increase the reach of PxD’s advisory to existing registered women AK users who may not be picking up the outbound advisory, but also extend the reach of our advisory to the wives and women children of men registered as AK users on the livestock service.
Adoption: Individual vs joint access to information
To better understand intra-household dynamics of information transmission and adoption, we asked respondents to the Gender Scoping Survey if they find it easy to convince their spouses to adopt new livestock practices when they receive such information. Of the respondents, 76% replied yes to this question, and we found no significant differences by gender. This percentage increased to 90% when we asked if listening to the advisory jointly with their spouses on the phone’s speaker would make it easier for them to adopt the recommended practices. A gendered analysis of this increase did not detect a statistically significant difference between men and women users.
Therefore, we find suggestive evidence that getting livestock recommendations to female farmers is the primary barrier to increasing the benefits accruing to our digital advisory. When women farmers receive advisory, they may be just as likely to influence adoption decisions as men farmers. Additionally, increasing the shared knowledge of the spouses has a greater potential to increase adoption rates than individual access to information.
Calibrating solutions
The phone’s speaker
One possible solution to reach more women farmers and promote information sharing among spouses is to encourage respondents who pick up advisory calls to use their phones’ speakers to listen to the advisory with other household members. We wanted to pilot a nudge to male livestock farmers to listen to advisory messages with their speakerphone turned on with other household members engaged in livestock-related activities. However, we first needed to know if farmers could use their phone’s speaker. We conducted a speakerphone feasibility survey to understand:
- Whether farmers can use their phone’s speaker by themselves.?
- If not, can we deliver simple instructions during the phone call so that farmers can use the phone’s speaker?
- Whether we need to build in a time allowance for farmers to activate their speaker and listen to advisory with their household members.? If so, then how much time?
- Whether farmers are willing to use their phone’s speaker and listen to the advisory with other household members.?
Of the 90 respondents who consented to the survey, 76.67% could turn on their phone’s speaker without any instructions (67.92% of feature phone users and 89.19% of smartphone users). Following simple instructions on how to use their speaker, 84.44% of respondents could do so. Overall, 89.19% of respondents were able to turn on their phone’s speaker within 10 seconds of being asked to do so, and of those, 96.2% were willing to use their phone’s speaker to listen to future AK advisory with their family members. As a consequence we are confident there are no large technical or aspirational barriers to adopting the nudge and we moved to pilot it in different forms.
Assessing potential interventions
These results encouraged us to test nudges in three ways for one month:
- A separate IVR nudge asking users to call into our inbound service for joint-listening over their speakerphone (n=600);
- A text 20 minutes before the weekly livestock advisory asking them to turn on their phone’s speaker and listen to the advisory with members of the household involved in livestock-related activities (n=500);
- An additional script at the start of the weekly livestock outbound with the same nudge as in Method 2 (n=500).
All the nudges were sent between 6 and 8 pm based on the findings on joint availability in the gender survey. Before implementing an A/B test to measure the effectiveness of these interventions, we conducted small pilots to select the most promising methods.
In the pilot, we did not find that nudging farmers to use the inbound services (Method 1) was very successful. We sent a nudge call to 600 farmers, asking them to dial a toll-free number to listen to the livestock advisory on the speakerphone with their family. A total of 12 people (and 14 total calls) dialed into the service within a week of the nudge, but none accessed the feature to listen to the livestock advisory. While this does not eliminate the possibility that nudged farmers discussed the call’s content with their spouses, we did not pursue this method to achieve the specific objective of joint listening.
For farmers who were nudged through an SMS (Method 2), using a short survey, we found that only 4% of respondents recalled the nudge’s content (n=126). We concluded that this method was unlikely to translate into increased joint-listening or improved knowledge and adoption.
Using another short survey, we found that farmers who were nudged in the introduction of the weekly livestock outbound advisory (Method 3) were 22 percentage points more likely to report having listened to the advisory message jointly with household members than those who received the regular outbound advisory (ntreatment = 61; ncontrol=45). As this method showed the most promise, we conducted an A/B test deploying it to 17,000 farmers over ten weeks starting in late October. We are currently reviewing data from this test and will share the learnings when they are available.
The authors would like to thank Qi Xue, PxD Intern, who offered valuable assistance in executing the surveys and preliminary analysis underpinning this post, as well as Niriksha Shetty, Tomoko Harigaya, and Otini Mpinganjira for their insights and guidance.
Appendix:
Make an Impact Today

